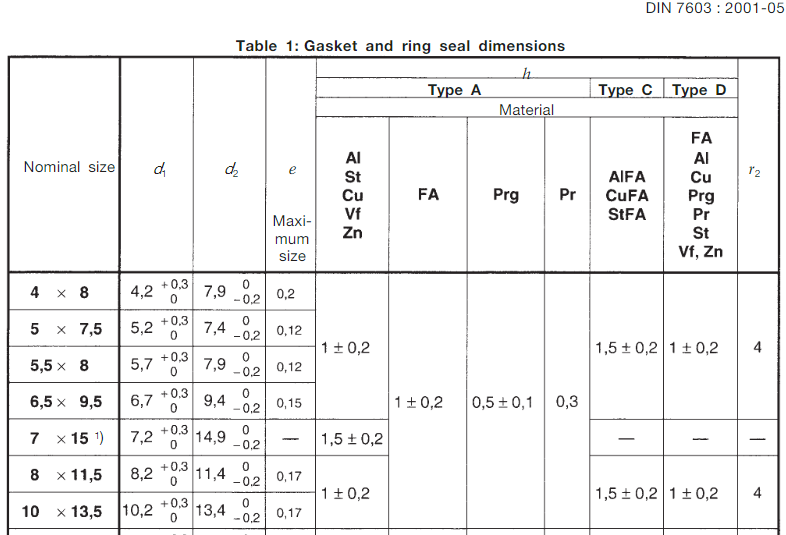
Sealing Rings In contrast to actual practice in standards published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), a comma has been used as the decimal marker. Introduction This Standard has been prepared by the Piping and Pressure Recipients Standards Committee. Amendments This Standard differs from the November 1994 edition as follows:
a) Dimensions and mass of O-rings and gaskets that will not be used for new designs are now covered in Appendix A.
b) Dimension r1 has been specified for type C joints.
c) The dimension d1 has been corrected for joints of nominal size 21 x 26.
d) The specifications relating to service temperatures have been modified (see table 3).
e) The standard has been editorially revised. Previous editions DIN 7603: 1936 -07, 1941 X-05, 1961 -01, 1961 -09, 1968-03, 1994-11. All dimensions are in millimeters 1 Scope This standard specifies dimensions and materials for ring seals and flat or filled gaskets, designed for use with compression couplings (for example, as specified in DIN 3850 or DIN 7601) or pipe or pipe plugs (as specified in DIN 908) couplings.
This standard incorporates, by dated or undated reference, provisions of other publications. These normative references are cited at the appropriate places in the text, and the publication letters are listed below. For dated references, subsequent amendments or revisions to any of these publications apply to this standard only when incorporated by amendment or revision. For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced publication applies. DIN 908 Threaded plugs with hexagon socket with parallel thread DIN 3850 Compression couplings - General description.
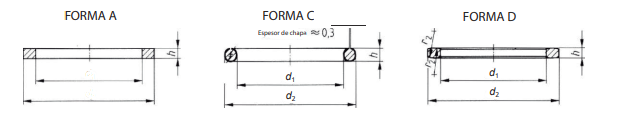
DIN 7603 FORM C
The metaloplastic joints are formed for a soul of soft material (FM, PTFE, GRAPHITE, etc.) partially or totally covered by a ductile metal sheet. The quality of materials for a board metaloplastic should be chosen according to of the working pressure and the fluid with the who will be in contact. Thanks to your understandable and lightweight structure are more indicated that the totally metallic in pressures and high temperatures. The boards Metalloplastics can be manufactured with one or several nerves arranged in different configurations They can be manufactured based on standards such as ASME 16.20 or according to specific specifications of client. The most commonly materials used for the manufacture of the joints Metalloplastics are like metallic material: copper, aluminum, AISI 304, 316L, 321, iron sweet and as a filling material: fiber mineral, graphite, PTFE, etc. he metaloplastic joints are manufactured in the most diverse circular, oval shapes, rectangular, square, rhomboids ... These boards have no size limit however, depending on the limitation of commercial ncho of materials, sometimes require the use of welding which is carried out following welding procedures approved. The standard thickness is 3.2 mm. although depending on the use, this It can be bigger or smaller.
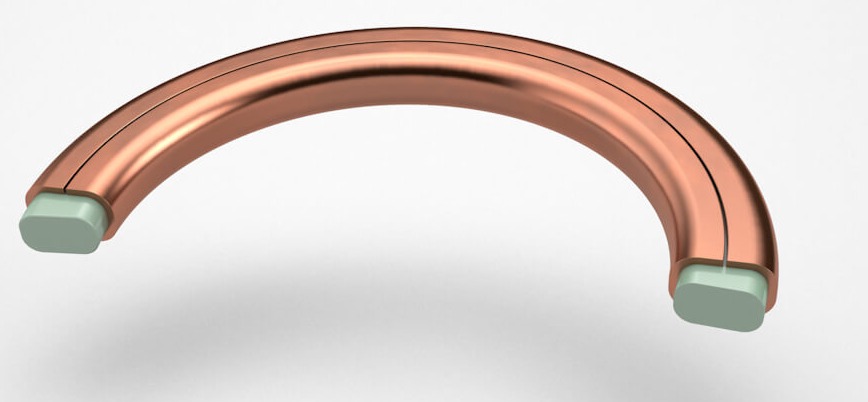
DIN 7603 FORM C WITH NERVES
On the occasion that the metalloplastic joint is without nerves (in one piece); in this case particularly the minimum radius of union of the nerve The ring is r = 10 mm. You have to have in account that the fabrication with welded nerves Not only is it more economical, technically it is superior, we carry a greater tightness, because in this case construction of the one-piece board that only has a closing line. For the assembly of the metal joint plastic in the team, you have to take account the deposition of the envelope and the lid in the tongue and groove pocket. According to the above, the side of the envelope must be installed towards the male and the side cap towards the cashier (female); If this does not happen, it could be damaged irreversibly the board when sinking prematurely cover.